Introduction
Design and technology is an inspiring, rigorous and practical subject. Using creativity and imagination, pupils design and make products that solve real and relevant problems within a variety of contexts, considering their own and others’ needs, wants and values. They acquire a broad range of subject knowledge and draw on disciplines such as mathematics, science, engineering, computing and art. Pupils learn how to take risks, becoming resourceful, innovative, enterprising and capable citizens. Through the evaluation of past and present design and technology, they develop a critical understanding of its impact on daily life and the wider world. High-quality design and technology education makes an essential contribution to the creativity, culture, wealth and well-being of the nation.
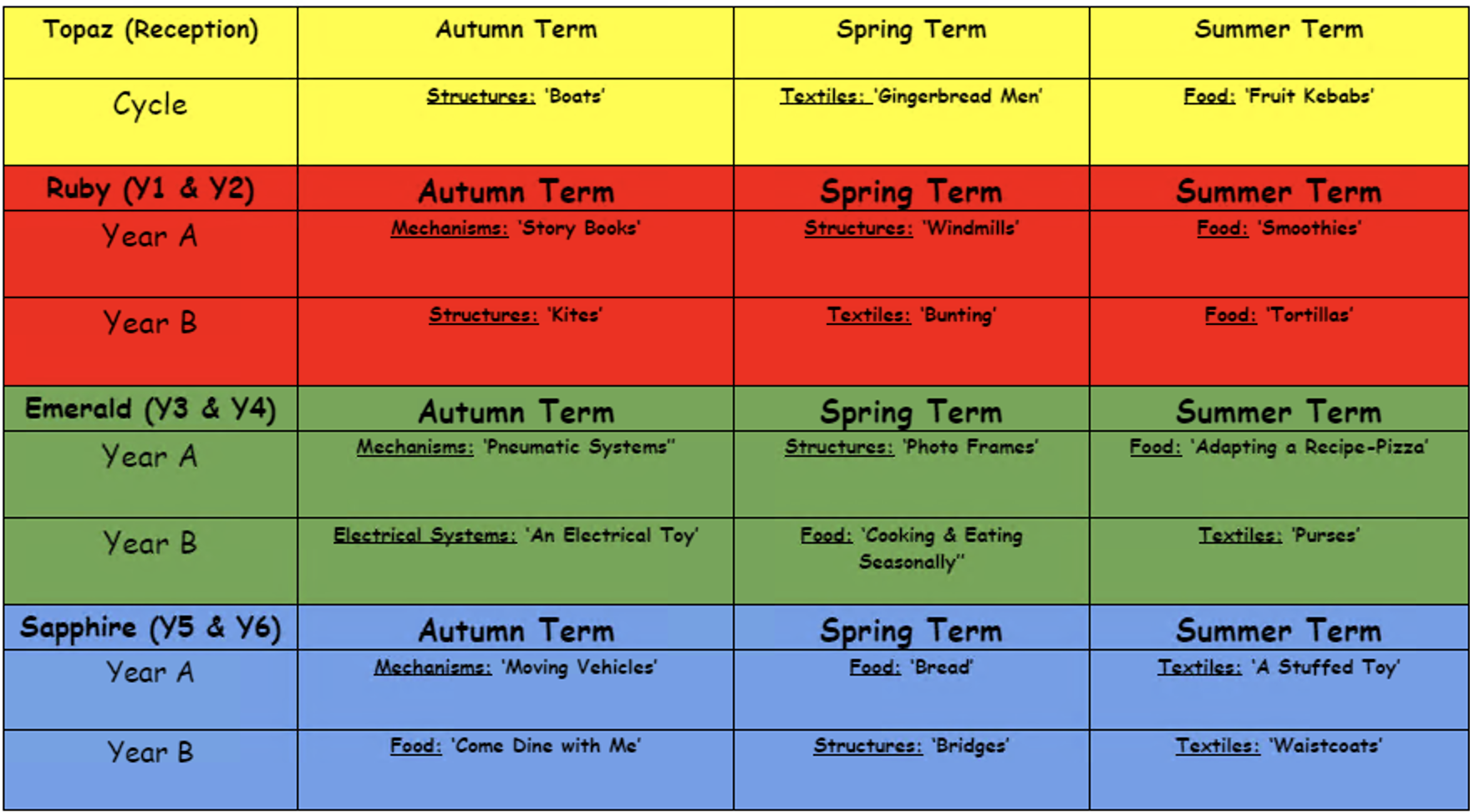
Design and technology is taught termly; in week-long blocks in most classes. This is so we can fully concentrate on the build up and progression of skills, knowledge and content, while not being distracted by the demands of other subjects.
Aims
The national curriculum for design and technology aims to ensure that all pupils:
- Develop the creative, technical and practical expertise needed to perform everyday tasks confidently and to participate successfully in an increasingly technological world
- Build and apply a repertoire of knowledge, understanding and skills in order to design and make high-quality prototypes and products for a wide range of users
- Critique, evaluate and test their ideas and products and the work of others
- Understand and apply the principles of nutrition and learn how to cook.
Attainment Targets
By the end of each key stage, pupils are expected to know, apply and understand the matters, skills and processes specified in the relevant programme of study.
Design and Technology Curriculum Objectives
EYFS
Design and technology in early years enables children to gain knowledge and understanding of their world. Design is not just about drawing, but about thinking. Creating fruit kebabs or designing a new Lego structure require no drawing, but both involve some experience, some imagination and a willingness to change and modify ideas.
Key Stage 1
Through a variety of creative and practical activities, pupils should be taught the knowledge, understanding and skills needed to engage in an iterative process of designing and making. They should work in a range of relevant contexts.
When designing and making, pupils should be taught to:
Design:
- Design purposeful, functional, appealing products for themselves and other users based on design criteria
- Generate, develop, model and communicate their ideas through talking, drawing, templates, mock-ups and, where appropriate, information and communication technology.
Make:
- Select from and use a range of tools and equipment to perform practical tasks
- Select from and use a wide range of materials and components, including construction materials, textiles and ingredients, according to their characteristics.
Evaluate:
- Explore and evaluate a range of existing products
- Evaluate their ideas and products against design criteria
- Build structures, exploring how they can be made stronger, stiffer and more stable
- Explore and use mechanisms in their products.
Key Stage 2
Through a variety of creative and practical activities, pupils should be taught the knowledge, understanding and skills needed to engage in an iterative process of designing and making. They should work in a range of relevant contexts.
When designing and making, pupils should be taught to:
Design:
- Use research and develop design criteria to inform the design of innovative, functional, appealing products that are fit for purpose, aimed at particular individuals or groups
- Generate, develop, model and communicate their ideas through discussion, annotated sketches, cross-sectional and exploded diagrams, prototypes, pattern pieces and computer-aided design.
Make:
- Select from and use a wider range of tools and equipment to perform practical tasks [for example, cutting, shaping, joining and finishing], accurately
- Select from and use a wider range of materials and components, including construction materials, textiles and ingredients, according to their functional properties and aesthetic qualities.
Evaluate:
- Investigate and analyse a range of existing products
- Evaluate their ideas and products against their own design criteria and consider the views of others to improve their work
- Understand how key events and individuals in design and technology have helped shape the world Technical knowledge apply their understanding of how to strengthen, stiffen and reinforce more complex structures.
Cooking and nutrition
As part of their work with food, pupils should be taught how to cook and apply the principles of nutrition and healthy eating. Instilling a love of cooking in pupils will also open a door to one of the great expressions of human creativity. Learning how to cook is a crucial life skill that enables pupils to feed themselves and others affordably and well, now and in later life.
Pupils should be taught to:
Key Stage 1:
- Use the basic principles of a healthy and varied diet
- To prepare dishes
- Understand where food comes from.
Key Stage 2:
- Understand and apply the principles of a healthy and varied diet
- Prepare and cook a variety of predominantly savoury dishes using a range of cooking techniques
- Understand seasonality, and know where and how a variety of ingredients are grown, reared, caught and processed.
Design & Technology Curriculum Planning
Due to having mixed aged classes, planning is carried out on a two year cycle to ensure continuity and progression so that children are challenged as they move up through the school. Differentiation is used to ensure all children are able to achieve, yet still be given the opportunity to be challenged. We acknowledge that pupils’ achievement is enhanced through lessons that are creative, active, where children are challenged and lead their own learning.
Inclusion
Our teaching of Design and technology forms part of the school ethos to provide a broad and balanced education to all children. To achieve this we provide learning opportunities that match the needs of all children and we take into account the targets set for individual children in their SEN Support Plans (IEPs). Planning, teaching and learning in Design and technology, sets high expectations for all children. Work is differentiated through content and by outcome to suit individual needs. It provides opportunities for all children to achieve including: boys and girls, children with SEN, children with disabilities, more able children, and children from all social and cultural backgrounds.
Teachers are aware that children bring to school different experiences, interests and strengths that will influence the way in which they learn. We recognise the fact that in all classes there are children of a variety of abilities and we seek to provide suitable learning opportunities for all children by matching the challenge of the task to the ability of the child.
Resources
The Design and technology lead is responsible for resourcing the DT curriculum. Resources are mostly kept centrally in the art cupboard.
Assessment
One of the important aspects of assessment is that it supports future planning and teaching of Design and technology. At St Bernadette’s assessment for learning (AFL) is integrated in all parts of the teaching and learning process.
The assessment of Design and technology is undertaken continuously by class teachers and other teaching staff whilst pupils are engaged in tasks.
Children’s work also provides evidence of learning and skills acquired. The cross-curricular nature of Design and technology means that children are able to explore themes, ask questions and problem solve through: MATHS, ICT, ENGLISH and ART.
Valuing children’s work is vital to their continued motivation, enjoyment and the empowerment of their learning and evidence of skills and understanding can therefore be sourced from a wide range of work – photographs, books, models, writing, art and videos of children’s work are displayed around school, on the website and stored on the server.